Last Updated on October 1, 2023 by Mark S. Taylor
The C1241 code in a Toyota indicates a low battery positive voltage problem. This fault code typically occurs when the vehicle’s battery voltage is too low.
With the increasing advancement in automotive technology, vehicles are becoming more complex and reliant on electrical systems. However, this also means that even the slightest issue with the electrical components can trigger a fault code. One such fault code is the C1241 code, which indicates a low battery positive voltage problem in a Toyota.
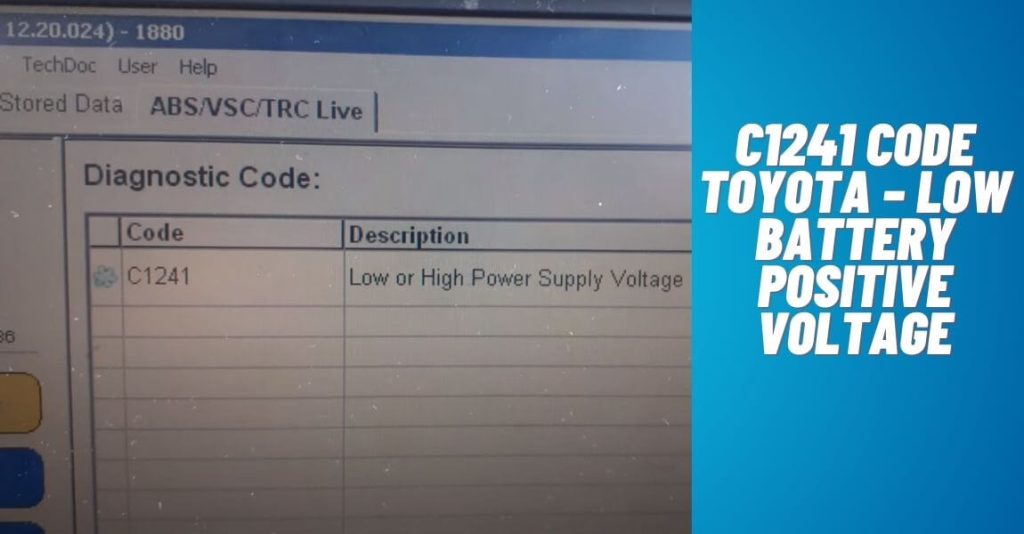
When the C1241 code appears, it generally means that the battery voltage is too low. This could be due to a weak battery, a faulty alternator, or a poor connection between the battery and the rest of the electrical system. In some cases, the code may also be triggered by a computer malfunction or a wiring issue. Regardless of the exact cause, it is crucial to address the C1241 code promptly. Ignoring it can lead to further electrical problems and potentially leave you stranded on the road. Therefore, it is advisable to have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional technician who can accurately pinpoint the underlying issue and carry out the necessary repairs. If you encounter the C1241 code in your Toyota, it indicates a low battery positive voltage problem. Seeking timely professional assistance is crucial to resolve the issue and ensure the smooth functioning of your vehicle’s electrical system.
Contents
Understanding The C1241 Code Toyota
Understanding the C1241 Code Toyota is essential for vehicle owners who encounter this issue. This code refers to a low battery positive voltage, which can cause various symptoms and warning signs. By familiarizing yourself with the possible causes and understanding the implications of this code, you can take the necessary steps to address the issue promptly and ensure the smooth operation of your Toyota vehicle.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
When your Toyota vehicle displays the C1241 code, it indicates an issue with the low battery positive voltage. Several symptoms and warning signs may accompany this code, which can help you identify the problem early on:
- Illumination of the check engine light: The check engine light is designed to alert you to any malfunction in your vehicle’s system. When the C1241 code is triggered, the check engine light may come on, indicating the low battery positive voltage issue.
- Difficulty starting the vehicle: A weak or low battery positive voltage can result in difficulties starting your Toyota vehicle. If you experience trouble turning on the engine or notice slow cranking, it could be a result of the C1241 code.
- Electrical system malfunctions: Low battery positive voltage can impact various electrical components in your vehicle. You may notice issues with the power windows, radio, or other electronic systems. Dimming headlights or flickering interior lights may also occur.
Possible Causes of the Issue
The C1241 code in a Toyota vehicle can stem from a variety of causes. It is important to consider these possibilities when diagnosing and addressing the low battery positive voltage issue:
- Faulty battery: Ensure that your vehicle’s battery is in good condition and functioning properly. A weak or faulty battery may not provide enough positive voltage, triggering the C1241 code.
- Loose or corroded battery connections: Check the battery terminals and connections for any signs of looseness or corrosion. A poor connection can hinder the battery’s ability to supply sufficient positive voltage, leading to the C1241 code.
- Starter motor issues: A malfunctioning starter motor can draw excessive power from the battery, resulting in low positive voltage. If the starter motor is faulty, it may need to be repaired or replaced.
- Bad alternator: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running. If the alternator is not functioning properly, it may not supply enough power to maintain sufficient positive voltage, causing the C1241 code.
- Wiring or electrical system faults: Faulty or damaged wiring, as well as issues within the electrical system, can disrupt the flow of positive voltage to the battery. Thoroughly inspect the wiring and consult a professional if necessary to address any potential faults.
By understanding the symptoms, warning signs, and possible causes of the C1241 code in your Toyota vehicle, you can take appropriate measures to resolve the low battery positive voltage issue. It is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic or technician for a proper diagnosis and efficient resolution to ensure the optimal functioning of your vehicle.
How To Diagnose The Low Battery Positive Voltage
Step-by-step guide to diagnosing the problem
When your Toyota vehicle encounters a C1241 code indicating low battery positive voltage, it is essential to diagnose the issue promptly. By following a step-by-step guide, you can effectively identify the root cause of the problem and take the necessary steps to resolve it. Here is a comprehensive guide to help you diagnose the low battery positive voltage issue in your Toyota:
- Check the battery voltage: Start by using a multimeter to measure the voltage of your car’s battery. A fully charged battery should typically register around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, it indicates a weak or discharged battery.
- Inspect the battery terminals: Examine the battery terminals and ensure they are clean and securely tightened. Corroded or loose connections can lead to low battery positive voltage. If you spot any corrosion, clean the terminals using a battery terminal cleaner and tighten them appropriately.
- Inspect the battery cables: Examine the battery cables for any signs of damage, such as fraying or exposed wires. Damaged cables can cause voltage drop, resulting in low battery positive voltage. If you notice any issues, replace the cables with new ones.
- Check the alternator: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine is running. A faulty alternator can lead to low battery positive voltage. Use a voltmeter to measure the voltage at the battery with the engine running. The voltage should ideally be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts. If the reading is below or above this range, it indicates a problem with the alternator.
- Inspect the battery condition: A worn-out or aging battery can contribute to low battery positive voltage. If your battery is more than three years old, it might be time to consider replacing it. Look for signs such as slow cranking or the need for frequent jump-starts.
- Perform a parasitic draw test: A parasitic draw occurs when there is an excessive power drain from the battery when the vehicle is turned off. Use a multimeter to measure the current draw when the car is off. If you notice a significant draw, it suggests a parasitic drain that needs further investigation.
Following these steps will help you accurately diagnose the low battery positive voltage issue in your Toyota vehicle. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for resolving the problem and ensuring your vehicle’s electrical system operates optimally. In case you encounter any difficulties or uncertainties during the diagnostic process, it is recommended to consult a professional technician or reach out to your local Toyota dealership for expert assistance.

Fixing The Low Battery Positive Voltage Issue
Fixing the Low Battery Positive Voltage Issue
If you own a Toyota vehicle and have recently encountered the C1241 code – Low Battery Positive Voltage, it’s important to address this issue promptly to ensure the optimal functioning of your vehicle’s electrical system. This code usually indicates a problem within the charging system or a low battery voltage causing the system to operate below the normal range. In this blog post, we will guide you through the steps to fix the Low Battery Positive Voltage issue.
<h3>Checking and replacing the battery</h3>
When facing the C1241 code, the first step is to check the condition of your vehicle’s battery. A defective or weak battery can cause low voltage, triggering this error code. Follow these steps to ensure your battery is in good working condition:
- Begin by inspecting the battery terminals for any signs of corrosion or loose connections. If there is corrosion, clean the terminals using a battery terminal cleaning brush and a mixture of baking soda and water.
- Next, test the voltage of the battery using a multimeter. A fully charged battery should measure around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is significantly lower, it may be time to replace the battery.
- If the battery is in good condition, proceed to inspect the charging system.
Replacing the battery is relatively simple and can be done using the following steps:
- Detach the negative terminal of the battery first, followed by the positive terminal.
- Remove any brackets or fasteners holding the battery in place.
- Take out the old battery and replace it with a new one of the same specifications.
- Secure the new battery in place by reattaching any brackets or fasteners.
- Reconnect the positive terminal first, followed by the negative terminal.
<h3>Inspecting and repairing the charging system</h3>
If the battery is not the culprit, the next step is to inspect the charging system. A faulty alternator or voltage regulator can cause low battery positive voltage issues. Follow these steps to inspect and repair the charging system:
- Start by visually inspecting the alternator and its connections. Look for any loose or damaged wires, as well as signs of wear or corrosion.
- Test the output voltage of the alternator using a multimeter while the engine is running. The voltage should read around 13.5 to 14.5 volts. If it’s significantly lower or higher, the alternator may need to be replaced.
- If the alternator is functioning properly, check the voltage regulator. Inspect it for any visible damage or loose connections. Consider replacing the voltage regulator if necessary.
- Additionally, check the condition of the drive belt that connects the alternator to the engine. If it’s worn or loose, it may not be adequately transferring power to the alternator.
- Repair or replace any damaged components identified during the inspection to ensure the charging system operates optimally.
<h3>Resetting the C1241 code</h3>
Once you have checked and addressed any issues with the battery and charging system, it’s essential to reset the C1241 code to ensure it doesn’t reappear unnecessarily. By following these steps, you can reset the code:
- Start by disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery, and wait for at least 15 minutes.
- While the battery is disconnected, turn on the vehicle’s headlights and leave them on for a few minutes. This will help discharge any remaining power in the system.
- After the waiting period, reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
- Start the vehicle and check for any remaining error codes. If the C1241 code does not reappear, it has been successfully reset.
Following these steps should help you fix the Low Battery Positive Voltage issue represented by the C1241 code in your Toyota vehicle. It’s essential to address this issue promptly to avoid further damage to the electrical system and ensure your vehicle operates smoothly. If you encounter any difficulties or the issue persists, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic or contact a Toyota service center for assistance.
Replacing The Battery
Having a reliable battery is crucial for the proper functioning of your Toyota vehicle. If you encounter the C1241 Code Toyota – Low Battery Positive Voltage, it is likely time for a battery replacement. When replacing the battery, there are various factors to consider to ensure you select the right battery for your Toyota, safely remove the old battery, and install the new one properly.
Selecting the right battery for your Toyota
Choosing the appropriate battery for your Toyota is essential to avoid further complications. To select the right battery, follow these steps:
- Identify the battery type: Determine the specific battery requirements based on your vehicle’s make and model. Consult your Toyota owner’s manual or check with a trusted mechanic for the correct battery type.
- Consider the battery size: Ensure the replacement battery has the correct dimensions and will fit properly in the designated battery tray of your Toyota. Pay attention to the overall size and terminal placement.
- Check the battery specifications: Look for information such as Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) and Reserve Capacity (RC). These specifications will help you find a battery with the necessary power to start your Toyota and meet your driving needs.
- Research battery brands and quality: Look for reputable battery brands known for their reliability and durability. Consider reading customer reviews and ratings to ensure you choose a high-quality battery.
- Compare prices: While it is important to find a battery within your budget, prioritize quality and performance. Avoid settling for a cheap battery that may not last as long or provide sufficient power.
Steps to safely remove the old battery
Before installing the new battery, it is crucial to safely remove the old one. Here are the steps to follow:
- Ensure the engine is turned off: Before removing the battery, make sure the engine is completely turned off. This will prevent any electrical mishaps.
- Protect yourself: Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect your hands and eyes from any potential hazards.
- Disconnect the negative terminal: Use a wrench or a socket to loosen and remove the negative (-) terminal clamp. This is usually marked with a black color or a minus sign.
- Disconnect the positive terminal: In the same manner, loosen and remove the positive (+) terminal clamp. This is typically marked with a red color or a plus sign.
- Remove the battery hold-down clamp: Depending on your Toyota model, there may be a hold-down clamp securing the battery in place. Remove the clamp using the appropriate tools.
- Remove the old battery: Carefully lift the old battery out of the battery tray, ensuring not to tip it or spill any fluids.
Installing the new battery properly
After successfully removing the old battery, it’s time to install the new one. Follow these steps to ensure a proper installation:
- Clean the battery tray: Before placing the new battery, clean the battery tray from any dirt, debris, or corrosion. This will help improve the connection and prevent any electrical issues.
- Place the new battery in the tray: Lower the new battery into the battery tray, ensuring it sits securely and evenly.
- Attach the hold-down clamp: If your Toyota has a battery hold-down clamp, reattach it to secure the battery in place.
- Connect the positive terminal: Attach the positive (+) terminal clamp to the corresponding battery post and tighten it securely.
- Connect the negative terminal: Similarly, connect the negative (-) terminal clamp to the appropriate battery post and tighten it firmly.
- Inspect the connections: Ensure that both terminal connections are stable and free of any corrosion. Tighten if necessary.
By following these steps, you can replace the battery in your Toyota properly and address the C1241 Code Toyota – Low Battery Positive Voltage issue. Remember to dispose of the old battery in an environmentally friendly manner and consult a professional if you face any difficulties during the process. A reliable battery will keep your Toyota running smoothly and ensure a hassle-free driving experience.
Inspecting And Repairing The Charging System
If you are encountering the C1241 code for low battery positive voltage in your Toyota vehicle, it is essential to inspect and repair the charging system to ensure optimal performance. The charging system is responsible for keeping the battery charged while the vehicle is running, and any issues can lead to power disruptions and potential breakdowns. In this section, we will explore the steps to test the alternator, check the voltage regulator, and repair or replace any faulty components.
Testing the Alternator for Proper Functioning
One of the first steps in diagnosing and addressing the low battery positive voltage issue is to test the alternator. The alternator is responsible for generating electrical power and charging the battery while the engine is running. To test the alternator, follow these steps:
- Start the vehicle and let it idle.
- Using a multimeter set to DC voltage, connect the positive (red) probe to the positive terminal of the battery and the negative (black) probe to the negative terminal. Make sure the engine is running.
- Note the voltage reading on the multimeter. It should be around 13.8-14.8 volts. Anything significantly lower or higher may indicate a problem with the alternator.
- If the voltage reading is within the acceptable range, it is likely that the alternator is functioning correctly. However, if the reading is outside the range, further inspection and potential repair or replacement of the alternator may be necessary.
Checking the Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator plays a crucial role in regulating the electrical output of the alternator and maintaining a stable voltage for the battery. A malfunctioning voltage regulator can cause issues with the charging system, leading to low battery voltage. Here’s how to check the voltage regulator:
- Locate the voltage regulator, which is typically integrated into the alternator.
- Inspect the wiring connections and ensure they are secure and free from any corrosion or damage.
- If the wiring connections are in good condition, use a multimeter to test the voltage regulator’s output. Set the multimeter to DC voltage and connect the probes to the appropriate terminals.
- The voltage reading should be within the manufacturer’s specified range. If the reading is outside the range or there is no output at all, the voltage regulator may need to be repaired or replaced.
Repairing or Replacing Faulty Components
If the alternator or voltage regulator is found to be faulty, it is crucial to repair or replace the affected components. Ignoring these issues can lead to further electrical problems and potentially a dead battery. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance to ensure you have the correct replacement parts.
- Disconnect the battery’s negative terminal to prevent any electrical shock or damage during the repair process.
- Remove the faulty alternator or voltage regulator following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Install the new component, ensuring all electrical connections are secure and properly tightened.
- Reconnect the battery and start the vehicle to verify if the low battery positive voltage issue has been resolved.
By inspecting and repairing the charging system, including testing the alternator, checking the voltage regulator, and addressing faulty components, you can effectively resolve the C1241 code for low battery positive voltage in your Toyota vehicle. This proactive approach ensures optimal performance and reliability while on the road.
Resetting The C1241 Code
Resetting the C1241 Code is an important step in troubleshooting and resolving issues related to the Low Battery Positive Voltage in Toyota vehicles. This code is commonly caused by a low voltage or faulty battery, and it can lead to various performance problems in the vehicle. Luckily, there are a few methods you can try to reset the C1241 code and get your Toyota back on track.
Clearing the code using an OBD-II scanner
One of the most effective ways to reset the C1241 code is by using an OBD-II scanner. This handheld device allows you to access the onboard computer system of your Toyota and read the stored fault codes. To clear the C1241 code using an OBD-II scanner, follow these steps:
- Locate the OBD-II port in your Toyota. It is usually found underneath the dashboard on the driver’s side.
- Plug the OBD-II scanner into the port and turn on the ignition.
- Follow the instructions provided by the scanner to access the diagnostic menu.
- Select the option to clear stored fault codes or reset the system.
- Wait for the scanner to complete the process, and then turn off the ignition.
This method is quick and efficient, but it does require an OBD-II scanner. If you don’t have access to one, you can try the alternative method of performing a battery disconnect procedure.
Performing a battery disconnect procedure
A battery disconnect procedure can also help reset the C1241 code in your Toyota. This method involves physically disconnecting the battery from the vehicle and waiting for a few minutes before reconnecting it. Here’s how you can perform a battery disconnect procedure:
- Ensure that the ignition is turned off and all electrical components are powered off.
- Open the hood of your Toyota and locate the battery.
- Using a wrench, loosen and remove the negative (-) battery cable from the battery terminal.
- Leave the battery disconnected for around 10-15 minutes.
- After the waiting period, reconnect the negative (-) battery cable to the battery terminal and tighten it securely.
- Close the hood and start the vehicle.
Performing a battery disconnect procedure allows the vehicle’s system to reset and clears any stored fault codes, including the C1241 code. It’s important to note that disconnecting the battery may cause the radio presets, clock, and other settings to reset. You may need to re-enter these settings after reconnecting the battery.
By following either of these methods, you can reset the C1241 code in your Toyota and improve the performance of your vehicle. However, it’s always recommended to consult a professional mechanic if the code persists or if you are unsure about performing the reset procedure yourself.
Preventative Measures To Avoid Recurrence
If you’ve experienced the C1241 Code Toyota – Low Battery Positive Voltage issue in your vehicle, it’s crucial to take preventative measures to avoid its recurrence. By implementing these measures, you can ensure that your battery remains healthy and the low battery positive voltage problem becomes a thing of the past. Here are three key preventative steps you can take:
Regular battery maintenance
Proper battery maintenance is essential for maximizing its lifespan and preventing voltage-related issues. Here are a few maintenance tips to keep your battery running smoothly:
- Inspect your battery regularly for any signs of damage, corrosion or leakage.
- Ensure that the battery terminals are clean and securely tightened.
- Keep the battery and its surrounding area clean and free from dust and debris.
- Check the battery’s fluid levels periodically and top up if necessary (for non-sealed batteries).
Checking the charging system periodically
The charging system of your vehicle plays a vital role in maintaining the battery’s charge. By regularly checking the charging system, you can identify any potential issues early on and prevent a low battery positive voltage problem. Here’s what you should do:
- Inspect the alternator and ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Measure the charging voltage to ensure it is within the recommended range.
- Check the condition of the drive belt and replace if worn out.
- Test the voltage regulator to ensure it is working properly.
Driving habits to preserve battery life
Your driving habits can greatly impact the life of your battery. By adopting certain habits, you can prolong its lifespan and minimize the risk of low battery positive voltage issues. Consider the following driving habits:
- Avoid leaving electrical accessories on when the engine is off, as this can drain the battery.
- Turn off headlights, cabin lights, and other electronic components when not in use.
- Try to minimize short trips and combine multiple errands into one, as frequent starts and stops can put a strain on the battery.
- Avoid using power-hungry features, such as seat warmers or high-powered audio systems, excessively.
By following these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing the C1241 Code Toyota – Low Battery Positive Voltage problem again. Remember, regular battery maintenance, periodic charging system checks, and adopting battery-friendly driving habits are key to keeping your battery healthy and your car running smoothly.
Conclusion And Final Thoughts
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the C1241 code in your Toyota is crucial for maintaining the overall health and performance of your vehicle. This blog post has provided valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, and solutions related to this code. Now, let’s quickly recap the main points discussed, emphasize the importance of addressing the code promptly, and provide some useful tips for maintaining a healthy battery in your Toyota.
Recap of the Main Points Discussed
- The C1241 code in Toyota vehicles indicates a low battery positive voltage.
- Common causes of this code include a weak or faulty battery, corroded or loose battery terminals, or a malfunctioning alternator.
- Symptoms of the C1241 code can range from a check engine light or ABS warning light, to issues with the vehicle’s braking system.
- To diagnose and resolve the C1241 code, it’s important to perform a battery voltage test, check the condition of the battery terminals, and inspect the alternator.
- Professional assistance may be required if the issue persists after performing basic troubleshooting steps.
Importance of Addressing the C1241 Code Promptly
Addressing the C1241 code promptly is essential for a smooth and safe driving experience. Ignoring the code can lead to potential risks and further damage to the vehicle. Here’s why it’s important to take action:
- Resolving the code helps to maintain the proper functioning of the electrical system, preventing any further damage to the vehicle’s components.
- It ensures the safety of both the driver and passengers by rectifying any potential issues related to the braking system.
- Timely resolution of the C1241 code can prevent additional costs and repairs that may be required if the problem persists.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Battery in Your Toyota
Maintaining a healthy battery is essential for the overall performance and longevity of your Toyota. Follow these simple tips to keep your battery in optimal condition:
- Regularly inspect the battery terminals for corrosion, and clean them if necessary. Tighten any loose connections to ensure a proper electrical connection.
- Check the battery’s electrolyte levels and top up with distilled water if needed. Be cautious not to overfill.
- Protect your battery from extreme temperatures by parking your vehicle in a shaded or covered area whenever possible. Extreme heat or cold can affect the battery’s performance.
- Test the battery voltage regularly to ensure it is within the recommended range. If the voltage drops below the specified level, consider replacing the battery to avoid further issues.
- Maintain a regular inspection schedule with a trusted mechanic to identify any potential battery or electrical system issues early on.
By following these tips and being proactive in addressing any battery-related issues, you can ensure a reliable and trouble-free driving experience in your Toyota.
Remember, addressing the C1241 code promptly and maintaining a healthy battery are essential for optimal vehicle performance and driver safety. Regular inspections, testing, and professional assistance when needed will help keep your Toyota running smoothly for years to come.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of C1241 Code Toyota – Low Battery Positive Voltage
What does FCW failed mean?
FCW failed is a warning message that appears in your car when there’s an issue with your Forward Collision Warning (FCW) system. This system is designed to alert you if it detects a potential collision with another vehicle or obstacle. When you see the “FCW failed” message, it means that the FCW system is not working correctly. This could be due to various reasons like dirty sensors, system malfunctions, adverse weather, or maintenance problems.
What does FCW system mean?
The FCW system stands for Forward Collision Warning System. It’s a safety feature in many modern cars. This system uses technology like radar and cameras to monitor the road ahead. Its main job is to keep an eye on the traffic in front of you. If it senses that you’re getting too close to the vehicle in front or if a collision is likely, it gives you a warning, such as a visual alert or a sound, to help you avoid an accident.
What does it mean when the FCW light comes on?
When the FCW light on your car’s dashboard comes on, it means that the FCW system is active and working. It’s like a little green or white indicator that tells you the FCW system is keeping an eye on the road for potential dangers. If it detects something that could lead to a collision, the light might change color to warn you.
What does FCW and LDW mean?
FCW and LDW are two different safety systems in cars. FCW, as mentioned earlier, is the Forward Collision Warning system, which helps prevent front-end collisions. On the other hand, LDW stands for Lane Departure Warning. This system monitors your vehicle’s position within your lane. If it detects that you’re drifting out of your lane without using your turn signal, it alerts you, usually with a warning light or sound. FCW and LDW work together to enhance safety on the road.
Conclusion
To summarize, the C1241 code in Toyota vehicles indicates a low battery positive voltage. This issue can lead to a variety of electrical problems, including the loss of power to critical systems in the vehicle. It is crucial to address this code promptly to prevent further complications.
By consulting a professional technician and taking appropriate measures, you can ensure the smooth functioning of your Toyota and avoid any potential breakdowns on the road.
